Product Management – “Mix of Art, Science, and Technology”
Product Management is a discipline, which can be justified by mixture of Art , science and Technology. As it involves developing and executing strategies to deliver successful products that meet customers’ needs and achieve business goals. In this blog, we will explore the different aspects of product management that will help you understand why do you need Product Manager for your Digital transformation projects and what value Product managers can bring to the table.
Product Vision and Strategy Development:
A Product Manager’s role includes establishing the product vision and ensuring that the strategy, which outlines how the vision will be realized, is coherent. The product vision forms the cornerstone of numerous crucial components of a product, such as the product strategy, product development roadmap, and product backlog and planning. All these aspects must be harmonized with the product vision. Having a well-crafted product vision can also make it simpler to define the above elements.
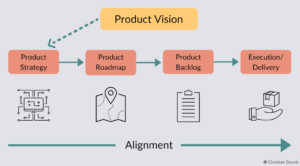
Roadmap Planning and Prioritization
Creating a product roadmap is a critical aspect of product management. It involves prioritizing features and product enhancements based on customer needs, market trends, and business objectives. A product manager must balance short-term goals with long-term strategic plans and communicate the roadmap to the cross-functional teams.
Prioritization can be challenging, after spending time in Product Roadmap and ideation, you are going to endup with lots of creative ideas, But you can’t use them all – You need to categorize, sort and select the idea that are most important , that is prioritization.
Prioritisation can:
- help quantify decisions and reduce the margin for error as you progress through the design process
- allow for different perspectives and expertise to be considered
- dilute the influence of senior leaders/strong opinions (sometimes known as HiPPO, the Highest Paid Person’s Opinion) by using data to inform decisions
- reveal patterns, themes or preferences and make them visible to the team and stakeholders, and
- stimulate discussion.
“Keep an eye for another post from D-BST Solutions for different Prioritization techniques“
Product Requirements Gathering and Documentation
The product manager is responsible for gathering and documenting product requirements. This involves working with cross-functional teams to identify the customer’s pain points, gather feedback from users, and create user stories that define product functionality.
User stories are a simple, yet powerful, technique used in Agile software development to describe a specific feature or functionality from the perspective of the end-user.User stories are typically written in a simple format: “As a (user type), I want to (goal or need) so that (reason or benefit).” For example, “As a customer, I want to be able to track the status of my order online, so that I can plan my schedule accordingly.”
The importance of user stories in Agile development lies in their ability to capture the user’s perspective and provide context to the development team. User stories help ensure that the focus of the product development is on meeting the needs of the users, rather than on building features that are not relevant or useful. User stories also help to break down complex features into smaller, more manageable pieces, making it easier for the development team to prioritize and plan their work.
Product Testing and Validation
Product testing and validation are critical in ensuring product quality. The product manager must work with the quality assurance team to define test cases, run tests, and ensure the product meets the customer’s requirements.
It also involves Prototyping and wireframing , These techniques allow the product manager to validate the product concept, test usability, and gather feedback from users. A product manager must be familiar with prototyping and wireframing tools to create a compelling product.
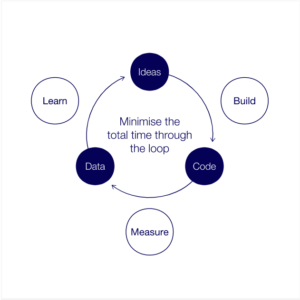
One of the most effective technique to validate user and product is [ Test, Build, Measure and Learn ]
The aim of these experiments is to facilitate a process of learning with minimal friction, transactional cost and effort.
In order to do this, you need to:
- Have an idea to test.
- Build a small prototype to test.
- Measure the results of tests with customers.
- Learn from the outcome.
“The below diagram from Lean Methodology shows by investing small amounts of resources early to test the hypotheses, Product Managers are able to gain confidence in their decision-making, moving forward with an initiative that has shown promising results in tests with customers, or stopping the investment in the development of features that have tested poorly.
Data Analytics and Metrics Tracking
Data analytics and metrics tracking are crucial in product management. The product manager must track product usage, user behavior, and other metrics to gain insights into customer needs, measure product performance, and identify areas for improvement.
Some of the Key metrics product manager should track are.
- User acquisition metrics: This includes metrics like the number of new users, user registration rate, and user retention rate. These metrics help to understand how effectively the product is attracting and retaining users.
- Engagement metrics: This includes metrics like the number of daily or monthly active users, user session duration, and user activity rate. These metrics help to understand how actively users are engaging with the product.
- Conversion metrics: This includes metrics like conversion rate, churn rate, and average revenue per user. These metrics help to understand how effectively the product is converting users into paying customers.
- Performance metrics: This includes metrics like website load time, app crash rate, and server uptime. These metrics help to understand how well the product is performing from a technical perspective.
- Customer satisfaction metrics: This includes metrics like Net Promoter Score (NPS), customer satisfaction (CSAT) score, and customer effort score (CES). These metrics help to understand how satisfied customers are with the product and their overall experience.
- Market share metrics: This includes metrics like market share, customer acquisition cost (CAC), and customer lifetime value (CLTV). These metrics help to understand how the product is performing in comparison to competitors.
- Development metrics: This includes metrics like cycle time, lead time, and velocity. These metrics help to understand how effectively the product development process is working and identify opportunities for improvement.
By tracking these metrics, a Product Manager can gain insights into the product’s performance and identify opportunities for improvement.
#ProductManagement #Agilemethodoloy #lean #Startup #Producideation #strategicConsulting
Follow D-BST Solutions https://dbstsolutions.com for more interesting topics
https://www.linkedin.com/company/d-bst-solutions/